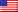
TFT LCD display is a thin film transistor type liquid crystal display, that is, “true color” (TFT). TFT liquid crystal is equipped with a semiconductor switch for each pixel, and each pixel can be directly controlled by dot pulse, so each node is relatively independent and can be continuously controlled, which not only improves the reaction speed of the display screen, but also accurately controls the display color scale, so the color of TFT liquid crystal is more true. TFT LCD is characterized by good brightness, high contrast, strong sense of hierarchy and bright colors, but it also has the disadvantages of relatively high power consumption and cost.
TFT (thin film transistor) is a kind of active matrix liquid crystal display. It can “actively” control each independent pixel on the screen, which can greatly improve the reaction time. Generally, the reaction time of TFT is relatively fast, about 80 milliseconds, and the viewing angle is large, which can generally reach about 130 degrees.
Polarity conversion mode of TFT LCD display:
The driving voltage of liquid crystal molecules cannot be fixed at a certain value, otherwise, as time goes by, the liquid crystal molecules will polarize and gradually lose their optical rotation characteristics. Therefore, in order to avoid the destruction of the characteristics of liquid crystal molecules, the driving voltage of liquid crystal molecules must be polarity changed, which requires the display voltage in the liquid crystal display screen to be divided into two polarity, one is positive polarity, the other is negative polarity. When the voltage of the display electrode is higher than that of the common electrode, it is called positive polarity; When the voltage of the display electrode is lower than that of the common electrode, it is called negative polarity. Whether it is positive or negative, there will be a group of gray scales with the same brightness, so when the absolute value of the pressure difference between the upper and lower layers of glass is fixed, the gray scales are exactly the same. However, in these two cases, the rotation of liquid crystal molecules is completely opposite, which can avoid the above-mentioned destruction of characteristics when the rotation of liquid crystal molecules is always fixed in one direction. There are four common polarity transformation modes, namely, frame by frame phase inversion mode, line by line phase inversion mode, column by column phase inversion mode and point by point phase inversion mode.
For the frame by frame inversion mode, in the same frame, all adjacent points of the whole picture have the same polarity, while the polarity of adjacent frames is different; For the line by line phase inversion mode, the same polarity exists on the same line, while the polarity of adjacent lines is different; For the column by column phase inversion mode, the same polarity exists in the same column, while the polarity of adjacent columns is different; For the point by point phase inversion mode, the polarity of each point is different from its adjacent upper, lower, left and right points.
At present, most of the panel polarity conversion methods used by the common personal computer LCD are point-by-point conversion methods. Why? The reason is that the display quality of phase inversion point by point is much better than other transformation methods. The table lists the performance comparison of four polarity transformation modes: frame by frame phase inversion, line by line phase inversion, column by column phase inversion and point by point phase inversion.
The so-called Flickr phenomenon is that the picture will flicker, but it is not a visual effect made deliberately, but because the gray scale of the displayed picture will change slightly every time the picture is updated, making the human eye feel that the picture is flickering. This is most likely to happen using the polarity transformation method of frame by frame phase inversion. Because the whole picture of phase inversion frame by frame is of the same polarity, when the picture is positive this time, it will become negative next time. If there is a little error in the common voltage, then the same gray-scale voltage of positive and negative polarity will be different. Of course, the feeling of gray-scale is also different, as shown in Figure 2. In the case of constantly switching pictures, the Flickr phenomenon will appear because the positive and negative pictures appear alternately. Although there will be such a Flickr phenomenon in the polarity transformation mode of other panels, it will not be obvious to the human eye because it is different from the frame by frame inversion, and the polarity of the whole picture changes at the same time, only one row or column, or even one point changes polarity.
The so-called crosstalk phenomenon refers to the fact that the data to be displayed between adjacent points will affect each other, so that the displayed picture will be incorrect. Although there are many causes of ctosstalk phenomenon, as long as the polarity of adjacent points is different, the occurrence of this phenomenon can be reduced.
Working principle of TFT LCD:
How does TFT work? TFT is the abbreviation of “thin film transistor”, which generally refers to thin-film liquid crystal display, but actually refers to thin-film transistor (matrix) – it can “actively” control each independent pixel on the screen, which is the origin of the so-called active matrix TFT. So how does the image come into being? The basic principle is very simple: the display screen is composed of many pixels that can emit light of any color. As long as you control each pixel to display the corresponding color, you can achieve the goal. In TFTLCD, backlight technology is generally used. In order to accurately control the color and brightness of each pixel, a switch similar to a shutter needs to be installed behind each pixel. When the “shutter” is opened, the light line can pass through, while when the “shutter” is closed, the light cannot pass through. Of course, technically, the implementation is not as simple as just said.
LCD (liquid crystal display) uses the characteristics of liquid crystal (it is liquid when heated and solid when cooled). Generally, liquid crystal has three forms:
Smectic liquid crystal similar to clay
Nematic liquid crystal similar to a thin matchstick
Cholesteric liquid crystal
The liquid crystal display uses filaments. When the external environment changes, its molecular structure will also change, so it has different physical properties – it can achieve the purpose of allowing light to pass or blocking light – that is, the shutter just mentioned.
You know the three primary colors, so each pixel on the display screen needs to be composed of three similar basic components introduced above, which control the red, green and blue colors respectively.
At present, twisted nematic TFT LCD is the most commonly used. The following figure explains the working principle of this kind of TFT display. The existing technologies are very different, and we will introduce them in detail in the second part of this article.
There are grooves on the upper and lower layers, of which the grooves on the upper layer are arranged vertically and the grooves on the lower layer are arranged horizontally. The lower layer is arranged horizontally. When the liquid crystal without voltage is in a natural state, the light emanating from the schematic layer of the twisted nematic TFT display working principle in the light-emitting figure 2A will be distorted by 90 degrees after passing through the interlayer, so that it can pass smoothly through the lower layer.
When a voltage is applied between the two layers, an electric field will be generated. At this time, the liquid crystals will be arranged vertically, so the light will not be twisted – as a result, the light cannot pass through the lower layer.
According to the color, color filters are divided into red, green and blue, which are arranged on the glass substrate in turn to form a group (dot pitch) corresponding to a pixel. Each monochromatic filter is called sub-pixel. In other words, if a TFT display supports 1280 at most × 1024 resolution, then at least 1280 is required × three × 1024 sub pixels and transistors. For a 15 inch TFT display (1024 × 768) then a pixel is about 0.0188 inch (equivalent to 0.30mm), for 18.1 inch TFT display (1280 × 1024), which is 0.011 inch (equivalent to 0.28mm). As we all know, pixels are decisive for the display. The smaller each pixel is, the larger the maximum resolution the display may achieve. However, due to the physical characteristics of transistors, the size of each pixel of TFT is basically 0.0117 inch (0.297mm), so for a 15 inch display, the maximum resolution is only 1280 × 1024。
Polarity conversion mode of TFT LCD panel:
The driving voltage of liquid crystal molecules cannot be fixed at a certain value, otherwise, as time goes by, the liquid crystal molecules will polarize and gradually lose their optical rotation characteristics. Therefore, in order to avoid the destruction of the characteristics of liquid crystal molecules, the driving voltage of liquid crystal molecules must be polarity changed, which requires the display voltage in the liquid crystal display screen to be divided into two polarity, one is positive polarity, the other is negative polarity. When the voltage of the display electrode is higher than that of the common electrode, it is called positive polarity; When the voltage of the display electrode is lower than that of the common electrode, it is called negative polarity. Whether it is positive or negative, there will be a group of gray scales with the same brightness, so when the absolute value of the pressure difference between the upper and lower layers of glass is fixed, the gray scales are exactly the same. However, in these two cases, the rotation of liquid crystal molecules is completely opposite, which can avoid the above-mentioned destruction of characteristics when the rotation of liquid crystal molecules is always fixed in one direction. There are four common polarity transformation modes, namely, frame by frame phase inversion mode, line by line phase inversion mode, column by column phase inversion mode and point by point phase inversion mode.
For the frame by frame inversion mode, in the same frame, all adjacent points of the whole picture have the same polarity, while the polarity of adjacent frames is different; For the line by line phase inversion mode, the same polarity exists on the same line, while the polarity of adjacent lines is different; For the column by column phase inversion mode, the same polarity exists in the same column, while the polarity of adjacent columns is different; For the point by point phase inversion mode, the polarity of each point is different from its adjacent upper, lower, left and right points.
At present, most of the panel polarity conversion methods used by the common personal computer LCD are point-by-point conversion methods. Why? The reason is that the display quality of phase inversion point by point is much better than other transformation methods. The table lists the performance comparison of four polarity transformation modes: frame by frame phase inversion, line by line phase inversion, column by column phase inversion and point by point phase inversion.
The so-called Flickr phenomenon is that the picture will flicker, but it is not a visual effect made deliberately, but because the gray scale of the displayed picture will change slightly every time the picture is updated, making the human eye feel that the picture is flickering. This is most likely to happen using the polarity transformation method of frame by frame phase inversion. Because the whole picture of phase inversion frame by frame is of the same polarity, when the picture is positive this time, it will become negative next time. If there is a little error in the common voltage, then the same gray-scale voltage of positive and negative polarity will be different. Of course, the feeling of gray-scale is also different, as shown in Figure 2. In the case of constantly switching pictures, the Flickr phenomenon will appear because the positive and negative pictures appear alternately. Although there will be such a Flickr phenomenon in the polarity transformation mode of other panels, it will not be obvious to the human eye because it is different from the frame by frame inversion, and the polarity of the whole picture changes at the same time, only one row or column, or even one point changes polarity.
The so-called crosstalk phenomenon refers to the fact that the data to be displayed between adjacent points will affect each other, so that the displayed picture will be incorrect. Although there are many causes of ctosstalk phenomenon, as long as the polarity of adjacent points is different, the occurrence of this phenomenon can be reduced.
Working principle of TFT LCD:
How does TFT work? TFT is the abbreviation of “thin film transistor”, which generally refers to thin-film liquid crystal display, but actually refers to thin-film transistor (matrix) – it can “actively” control each independent pixel on the screen, which is the origin of the so-called active matrix TFT. So how does the image come into being? The basic principle is very simple: the display screen is composed of many pixels that can emit light of any color. As long as you control each pixel to display the corresponding color, you can achieve the goal. In TFTLCD, backlight technology is generally used. In order to accurately control the color and brightness of each pixel, a switch similar to a shutter needs to be installed behind each pixel. When the “shutter” is opened, the light line can pass through, while when the “shutter” is closed, the light cannot pass through. Of course, technically, the implementation is not as simple as just said.
LCD (liquid crystal display) uses the characteristics of liquid crystal (it is liquid when heated and solid when cooled). Generally, liquid crystal has three forms:
Cholesteric liquid crystal
Nematic liquid crystal similar to a thin matchstick
Smectic liquid crystal similar to clay
The liquid crystal display uses filaments. When the external environment changes, its molecular structure will also change, so it has different physical properties – it can achieve the purpose of allowing light to pass or blocking light – that is, the shutter just mentioned.
You know the three primary colors, so each pixel on the display screen needs to be composed of three similar basic components introduced above, which control the red, green and blue colors respectively.
At present, twisted nematic TFT LCD is the most commonly used. The following figure explains the working principle of this kind of TFT display. The existing technologies are very different, and we will introduce them in detail in the second part of this article.
There are grooves on the upper and lower layers, of which the grooves on the upper layer are arranged vertically and the grooves on the lower layer are arranged horizontally. The lower layer is arranged horizontally. When the liquid crystal without voltage is in a natural state, the light emanating from the schematic layer of the twisted nematic TFT display working principle in the light-emitting figure 2A will be distorted by 90 degrees after passing through the interlayer, so that it can pass smoothly through the lower layer.
When a voltage is applied between the two layers, an electric field will be generated. At this time, the liquid crystals will be arranged vertically, so the light will not be twisted – as a result, the light cannot pass through the lower layer.
According to the color, color filters are divided into red, green and blue, which are arranged on the glass substrate in turn to form a group (dot pitch) corresponding to a pixel. Each monochromatic filter is called sub-pixel. In other words, if a TFT display supports 1280 at most × 1024 resolution, then at least 1280 is required × three × 1024 sub pixels and transistors. For a 15 inch TFT display (1024 × 768) then a pixel is about 0.0188 inch (equivalent to 0.30mm), for 18.1 inch TFT display (1280 × 1024), which is 0.011 inch (equivalent to 0.28mm)