1. LCD
wants to clarify the matter of these screens, but also to start with the LCD screen. The LCD panel industry is now becoming increasingly unprofitable. Samsung and LG Display have significantly reduced LCD production lines, and Panasonic has simply withdrawn from the LCD field. (The most outdated screen, but it is indeed my favorite screen, purely personal hobby.) Let’s briefly talk about the working principle of LCD.
LCD working principle:
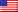
Under the LCD layer is a backlight, which emits white light. The upper layer is the RGB polarizing layer. The pass rate of RGB tricolor light can be controlled by adjusting the polarized light.
Look at the picture below: the back light is turned on, the screen will light up; if the back light is turned off, the screen will be black if it doesn’t emit light.
2. When LED
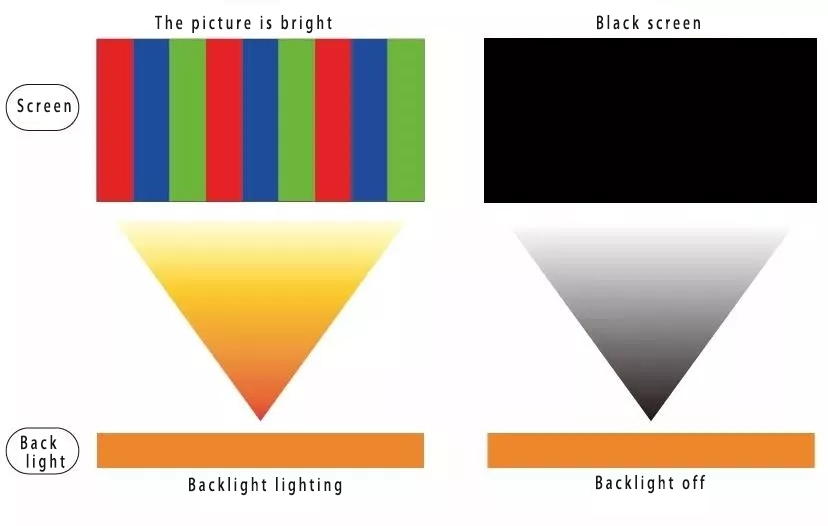
talks about the backlight, you can continue to talk about the LED screen. The biggest difference between it and LCD is this backlight. LCD uses cold cathode fluorescent tubes, as shown on the left side of the figure below, it seems that there are many fluorescent lamps installed. The LED screen uses LEDs encapsulated one by one on the PCB as the backlight (now industrial displays also have glass backplanes).
Look at the right side of the comparison chart below. This LED picture is probably familiar to everyone. The LED chandelier is probably long like this.
Here comes the question: people often dislike LCD and say that the contrast is not enough, because there is no way to make it completely black. Why?
Answer: The LCD backlight is always on, and the partial brightness of the screen is realized by the front LCD screen. The screen will also be transparent, right?
Therefore, the advantages of the LED screen can be reflected at this time. The LED screen can precisely control where to light up.
Micro LED
Micro LED , the size is reduced by half compared with Mini LED , about 50 microns. Both high resolution and high response speed are better than OLED . The power consumption is 90% lower than that of LCD and 50% lower than that of OLED . Low power consumption, which means power saving .
And life than OLED longer , because OLED inside the O , Organic , represented is the use of organic materials is finite life, which is often said that the concerns of screen burn. For Micro LEDs , inorganic gallium nitride materials are used, which is fine. Micro LED is technically different from Mini LED . It does not rely on backlight technology. It is similar to OLED ‘s self-luminous. Micro LED has three self-luminous Micro LED industrial displays in each pixel .
At present, the biggest difficulty of Micro LED is the so-called » mass transfer » . What does it mean? In terms of technology, Micro LED panels must first be processed with LED chips, and then the LEDs are transferred to the substrate one by one. This process is called » mass transfer » .
Why is this » mass transfer » difficult?
Answer: Let’s take a 4K panel as an example, 3840×2160 , with 8 million pixels, and each pixel has three LEDs , so as many as 24 million Micro LEDs are needed . If calculated according to the yield rate of 99.99% , a panel has 2400 dead pixels.
You may think whether the current OLED is also of such a high density, but it is not. OLED adopts the PENTILE arrangement, that is, adjacent pixels will share an OLED . Anyway , what I want to talk about is Micro LED , which is a very good, hope for the future, but the current process is not easy. Large screens are not available now, but small sizes are still possible. For example, wearable consumer electronics, mobile phones or watches are currently the most widely used areas of Micro LED display technology .
in conclusion:
The ultimate goal of Micro LED in the future,
Mini LED is currently the most promising transition solution.